Easy way to configure DAG Networking with Exchange 2010
Today, despite of high security measures taken, database on a server is still vulnerable to disasters & breakdowns. Having multiple copies of our database can help access it anyhow. In Exchange 2007, there is a functionality known as CCR (Cluster Continuous Replication). In which two copies of a database are maintained. This functionality is extended in MS Exchange 2010 and got named as Database Availability Group. Many replicas of your database are maintained on different servers with the help of it. By using this feature of Exchange 2010, database can be accessed even in downtime.
What is a DAG?
It is a collection of servers that can host an updated copy of mailbox database. Therefore, it gives high availability of data for its user. Member server of DAG having the ability of hosting passive or active copies of mailbox database which are present on servers in the group.
For example, A DAG is made up of three Exchange 2010 mailbox servers, each builds with a single mailbox database. Each member server of it can host either a passive copy or an active copy of any of the three mailbox databases.
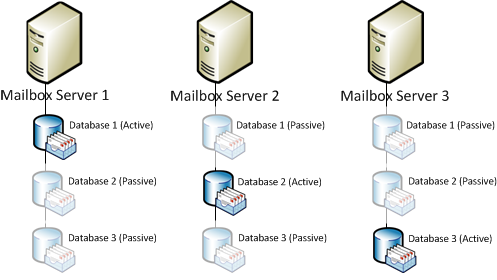
Fig: illustrate DAG
Advantages of Database Availability Group
- Automatic Failover
- Provides a high availability solution without any complexity like Failover Cluster and Storage Area Network. So it is easy to deploy it.
- DAG support incremental deployment, that means you can add or remove members from the server. You can also modify which server is a member of it or which mailbox data is being replicated. For this change, you need not to remove but modify it in existing DAG.
- An Exchange 2010 can host multiple DAGs. But a server is a member of only one Database Availability Group.
Note: Before adding members to the Availability Group, you must create it in Exchange organization.
- Failover Cluster
In DAG the servers are arranged in the form of clusters. Nodes (also called a cluster server) provide a distributed namespace and clustered shared volume, that clustered roles can use to access shared or physical storage space where copy of data is store.
Failover Cluster is created and configured automatically as soon as you create a Database Availability Group.
- Active Manager
- It is a core member of a DAG.
- It is an internal component of Exchange 2010 which manages Failover and Switchover. It inspects which server is failing and when a Switchover is performed.
- This core part runs on every member server of DAG.
- Detects failure of local servers and initiates the Failover.
- Forward the info to the Client Access Server to aware them, which served with a DAG host an active copy of a specific mailbox.
- And it's a key part that an Exchange Administrator doesn't need to directly interact with the active manager in order to manage DAGs. It's only create and manage servers in a database availability group.
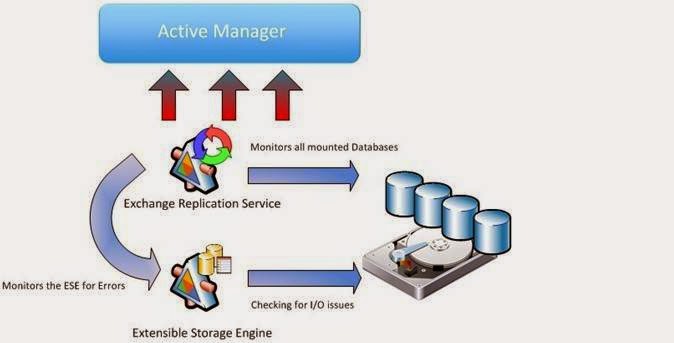
Fig: Active Manager
- Witness Server & Witness Directory
- A witness Server is a Hub Transport Server that does not install Mail Server. Also, a directory over witness server called Witness Directory, is made to maintain the witness server info.
- As the mailbox server role is not installed over witness server, it is not considered as a part of the DAG.
- Witness Server must be a member of the same Active Directory forest as DAG.
- If you don't specify a witness server during DAG creation, it automatically searches a Hub Transport Server without mailbox server role, creates a witness directory, and configures it as a witness server.
- The file share witness, is a file share on a server outside of DAG.
Step by step procedure to Configure DAG NETWORKING WITH MS EXCHANGE 2010:
Here, in this article, I will explain how to create, add, and manage new Database Availability Groups in Exchange Server 2010 SP1 on a Windows Server 2008 R2.For my scenario, following Exchange Servers with primary and secondary interface, have already been installed:
EX1 – Exchange Server 2010 SP1 Mailbox serverEX2 – Exchange Server 2010 SP1 Mailbox serverEX3 – Exchange Server 2010 SP1 Client Access and Hub Transport server
Fig1: Setup of Exchange 2010 DAG
Each Mailbox server is configured with its mailbox database:EX1 – Mailbox Database 01
EX2 – Mailbox Database 02
Note: Each mailbox must have unique names in the organization.
As two interfaces are configured with mailbox server, so you have to make sure that, in DNS, secondary interface is not configured itself. For this, use the following steps:

Fig: Disable DNS registration for the secondary interface
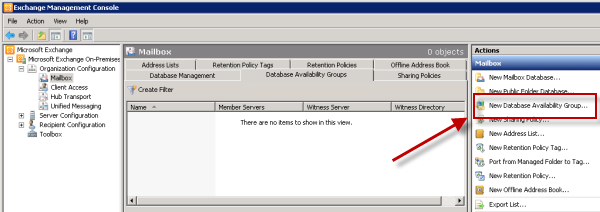
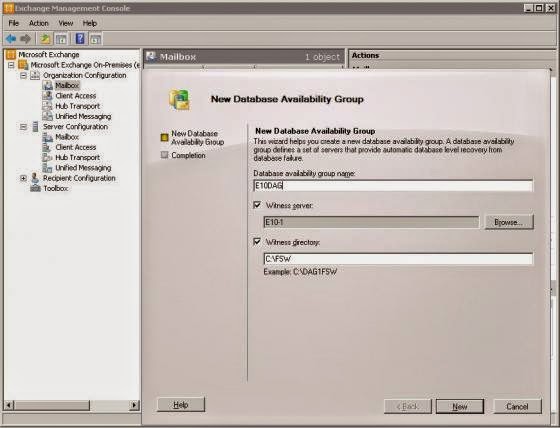
Fig: Provide the name of the DAG and related server
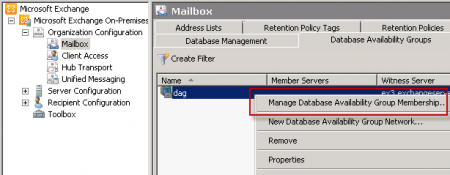
Fig: Adding DAG members

Fig: Select Mailbox Servers to become Database Availability Group Members
Click on Manage button to add the Mailbox servers to the DAG. This includes configuration and installation of failover clustering on servers, so it may take some time to complete.
After finishing the process, next configure the database availability group networking.

Fig: Open the Properties
Now,

Fig: Adding IP addresses to an Exchange Server 2010 availability Group
Notice that the Database Availability Group has been configured automatically with DAG networks for the subnet and the network interfaces connected with its members.

Fig: Exchange Server 2010 group Networks
Now,for each DAG network, open Properties and configure with logical names.
For configuring a dedicated replicated network for DAG, you must disable replication over DAG network that is proposed for client connection (i.e.MAPI Communication).
Exchange Server 2010 Database Availability Group Networks Configured
Adding Mailbox Database copies to DAG members
After establishing and configuring network, you can now add mailbox database replica to DAG members.Follow the steps:

Fig: Adding a Mailbox Database Copy in Exchange Server 2010
Click on Browse and select the mailbox server, you wish to add the database copy in.
Fig: Add Mailbox Database Copies to an Exchange 2010 Mailbox Server
For adding a mailbox database copy, click ADD and then Finish to complete the process.
The Exchange will now start to make replica servers with an updated copy of your database and all current transaction log files. Time to replicate data depends on the amount of information.
Fig: Status of the Database Copies for Exchange Server 2010
Follow the same process as above to add any mailbox database copies to Exchange mailbox server. After this the whole configuration of Exchange 2010 DAG is accomplished.
Conclusion:
Microsoft gives mailbox database high availability feature in Exchange 2010.From the above information, you should be fully aware that the DAG gives highly availability of database.Other components, such as the Hub Transport role,Client Access Server role,Active Manager, DNS,Witness server and so on.
As two interfaces are configured with mailbox server, so you have to make sure that, in DNS, secondary interface is not configured itself. For this, use the following steps:
- On each server, for the secondary interface, open TCP/vIP4 properties.
- Click on the Advance button.
- Navigate to DNS tab and uncheck Register this connection's address in DNS.

Fig : Open the Advanced TCP/IPv4 Properties.

Fig: Disable DNS registration for the secondary interface
Create the New Database Availability Group
Go to the Mailbox servers and open the Exchange Management Console.- Navigate to Organization Configuration then Mailbox.
- Select New DAG.
- Name it.


Fig: Provide the name of the DAG and related server
Managing Member In Availability Group
- Go to Organization Configuration, navigate to Mailbox.
- Right click on the new DAG and select Manage "Database Availability Group Membership".

Fig: Adding DAG members
- Click on the Add button.
- Select the mailbox servers that you want to make members of the DAG.

Fig: Select Mailbox Servers to become Database Availability Group Members
Click on Manage button to add the Mailbox servers to the DAG. This includes configuration and installation of failover clustering on servers, so it may take some time to complete.
After finishing the process, next configure the database availability group networking.
Configuring DAG Networking
- Again right click on newly created DAG.
- Select Properties.

Fig: Open the Properties
Now,
- Select IP Addresses tab.
- Click Add button, add a static IP address to the DAG.

Fig: Adding IP addresses to an Exchange Server 2010 availability Group
Notice that the Database Availability Group has been configured automatically with DAG networks for the subnet and the network interfaces connected with its members.

Fig: Exchange Server 2010 group Networks
Now,for each DAG network, open Properties and configure with logical names.
For configuring a dedicated replicated network for DAG, you must disable replication over DAG network that is proposed for client connection (i.e.MAPI Communication).
Exchange Server 2010 Database Availability Group Networks Configured
Adding Mailbox Database copies to DAG members
After establishing and configuring network, you can now add mailbox database replica to DAG members.Follow the steps:
- In EMC, navigate to Organization Configuration and then to, Mailbox.
- Choose Database Management tab.
- Right-click on a mailbox database and select Add Mailbox Database Copy.

Fig: Adding a Mailbox Database Copy in Exchange Server 2010
Click on Browse and select the mailbox server, you wish to add the database copy in.

Fig: Add Mailbox Database Copies to an Exchange 2010 Mailbox Server
For adding a mailbox database copy, click ADD and then Finish to complete the process.
The Exchange will now start to make replica servers with an updated copy of your database and all current transaction log files. Time to replicate data depends on the amount of information.

Fig: Status of the Database Copies for Exchange Server 2010
Follow the same process as above to add any mailbox database copies to Exchange mailbox server. After this the whole configuration of Exchange 2010 DAG is accomplished.
Conclusion:
Microsoft gives mailbox database high availability feature in Exchange 2010.From the above information, you should be fully aware that the DAG gives highly availability of database.Other components, such as the Hub Transport role,Client Access Server role,Active Manager, DNS,Witness server and so on.















0 comments:
Post a Comment
Post a reply